Industrial Hygiene Concerns in Healthcare
Maintaining a robust industrial hygiene program is important in any industry, and healthcare is no exception. A number of substances that contribute to a hospital’s ability to provide quality healthcare to patients can also have adverse health effects on the employees who handle them which is why creating an industrial hygiene program with the help of a certified industrial hygienist is important.
Common Substances of Concern in Healthcare Workplaces
When determining which clinical healthcare employees to monitor for exposure to hazardous chemicals, two primary areas should be considered:
- Pathology Labs
- Operating Rooms
Dangerous Substances in Pathology Labs
In Pathology labs, materials of particular concern are xylene and formaldehyde. While its popularity has been declining as labs opt for safer alternatives, xylene is still used in the processing and staining of tissue specimens for histopathology. While it is useful for this purpose, xylene is known to be toxic when inhaled, affecting the respiratory and nervous systems in particular. The OSHA Permissible Exposure Limit (PEL) for xylene is 100 parts per million (PPM).
Formaldehyde is another chemical commonly handled in Pathology labs, used for fixing and preserving tissue specimens. While formaldehyde is usually used in the form of buffered formalin solution, in which the concentration of formaldehyde is low, the OSHA formaldehyde standard (29 CFR 1910.1048) still applies. Included in this standard is a requirement that covered employers monitor their employees’ exposure to the chemical. This is because it is known to have both acute effects on the respiratory system as well as carcinogenic effects after chronic exposure. The OSHA PEL for formaldehyde is 0.75 PPM.
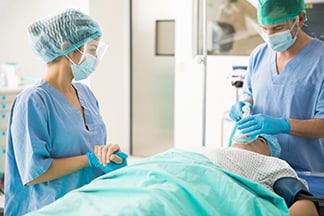
Dangerous Substances in Operating Rooms
The Operating Room also presents exposure hazards to employees, and industrial hygiene monitoring should be considered for waste anesthetic gases. These are anesthetic gases that either leak from the apparatus delivering them to the patient, or that are exhaled by patients after surgery. They include nitrous oxide and halogenated anesthetic gases, among which desflurane and sevoflurane tend to be common.
While OSHA has not established exposure limits for anesthetic gases, inspectors may still issue citations under the General Duty Clause making reference to limits set in consensus standards, like those published by the National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH) and the American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists (ACGIH).
Acute inhalation exposure to nitrous oxide can lead to dizziness, unconsciousness, and death. Chronic exposure can lead to infertility. NIOSH has recommended an 8-hour time weighted average exposure limit of 25 PPM. Additionally, the ACGIH has established an 8-hour time weighted average exposure limit of 50 PPM.
Halogenated anesthetic gases, such as desflurane, sevoflurane, halothane, enflurane, and isoflurane, are used as general anesthesia in operating rooms. Acute exposure to halogenated anesthetic gases can cause headaches, drowsiness, and impair decision-making and coordination, while chronic exposure at high concentrations can have carcinogenic or adverse reproductive effects. NIOSH has recommended that an exposure level of 2.0 PPM is never exceeded over a one-hour sampling period, and ACGIH has promulgated 8-hour time-weighted average recommended exposure limits for similar gases halothane and enflurane of 50 PPM and 75 PPM, respectively.
Putting an Industrial Hygiene Program in Place
Healthcare facilities must maintain a high standard of care for their patients while taking steps to ensure the safety of their employees. Developing, implementing, and enforcing a comprehensive industrial hygiene program is critical to the health and safety of your staff. Our Certified Industrial Hygienists and experienced environmental health and safety consultants can evaluate your existing IH program, design a new one, or provide guidance on how to properly execute and manage your program. Contact our IH experts today.